Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The bond energies of the reactants in the manufacture of ammonia for fertilizer
were too high to produce suitable quantities of ammonia. To overcome this obstacle,
chemists
a. | added a catalyst | b. | added an inert gas | c. | changed the
concentrations of the reactants | d. | changed the concentration of the product by
removing it |
|
|
|
2.
|
The equilibrium constant for a given reaction will be the same, regardless of
the initial concentrations, but only if the environmental conditions remain the same. Why?
a. | The order of the reaction remains constant. | b. | The number of
collisions remains constant, regardless of concentration. | c. | The reaction rate is
constant. | d. | The product concentration will be similarly affected by increases or decreases in
reactant concentration. |
|
|
|
3.
|
The equilibrium constant for the production of ammonia gas was 1.02 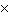
10 –5 at 300 °C. The equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction would
be a. | The equilibrium constant cannot be determined without the initial and final
concentrations. | b. | 9.8 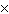 104 104 | c. | 9.8 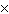 10–5
10–5 | d. | 1.02 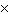 10–5
10–5 |
|
|
|
4.
|
Suppose the equilibrium constant for the production of ammonia gas is 4.26 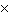
10 8 at 25 °C. This reaction’s equilibrium position is a. | to the left | b. | near the centre | c. | to the
right | d. | undetermined |
|
|
|
5.
|
Hydrogen carbonate exists in equilibrium with carbon dioxide and water inside of
a soda can. What will happen to the equilibrium if you shake the can?
a. | The equilibrium will shift to the right. | b. | The equilibrium will
not change. | c. | The equilibrium will shift to the left. | d. | The equilibrium will
shift to the centre. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Methanol is widely used as an industrial solvent. Methanol’s production is
given by the following formula: CO(g) + 2 H 2(g) « CH 3OH(l), 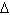 H H= –238.7 kJ/mol How
would a high temperature affect this equilibrium? a. | It would favour the production of methanol. | b. | It would not affect
this equilibrium as the number of atoms is equal on both sides. | c. | It would favour the
production of the reactants. | d. | It would be in the central position because the
quantity of reactants and products are at equilibrium together. |
|
|
|
7.
|
The trial ion product, Q, when compared to the Solubility Product
Constant, Ksp, will indicate if the final products will be insoluble. The
equilibrium will shift left if Q is
a. | equal to Ksp | b. | less than
Ksp | c. | 100 times less than the value of
Ksp | d. | greater than
Ksp |
|
|
|
8.
|
What will happen to the following equilibrium if silver ions are added to the
solution? AgNO3(s) «
Ag(aq) + NO3(aq)
a. | There will be no change. | b. | The equilibrium will shift to the
right. | c. | The equilibrium will shift to the left. | d. | The equilibrium will
shift to the centre. |
|
|
|
9.
|
In biochemical reactions, a buildup of the products of a reaction often causes
the reverse reaction to occur. This reduces the quantity of product. This process is referred to as a
negative feedback loop. This adjustment in the equilibrium is also known as
a. | Le Chatelier’s principle | b. | Dalton’s law of partial
pressures | c. | the law of mass action | d. | collision
theory |
|