Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
An exothermic reaction is carried out in an closed system and an isolated
system. Which of the following is true?
a. | There will be no temperature change in the isolated system, since heat can not move
into or out of the system. | b. | The temperature change in the isolated system
will be greater than the temperature change in the closed system. | c. | The temperature
change in the closed system will be the same as the temperature change in the isolated system.
| d. | The temperature change in the closed system will be greater than the temperature
change in the isolated system. |
|
|
|
2.
|
This illustration shows the energy change during the following
reaction: CH 4(g) + 2 O 2(g) ®
CO 2(g) + 2 H 2O(g) 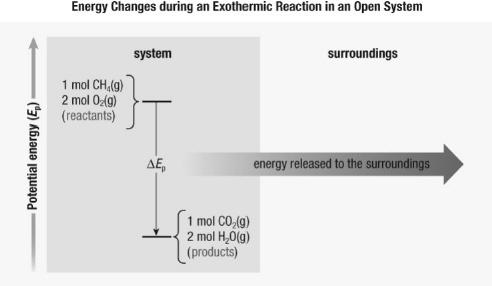 Which statement is
true? a. | The products contain more energy than the reactants. | b. | The reactants
contain more energy than the products. | c. | The potential energy of the system is
increasing. | d. | No energy changes are occurring. |
|
|
|
3.
|
A chemical reaction is carried out in a coffee cup calorimeter. The temperature
of the water changes from 25.2 °C to 19.8 °C. Which statement is correct?
a. | The water loses energy, so the reaction is exothermic. | b. | The water gains
energy, so the reaction is exothermic. | c. | The water loses energy, so the reaction is
endothermic. | d. | The water gains energy, so the reaction is
endothermic. |
|
|
|
4.
|
What quantity of heat is required to raise the temperature of 2.0 g of iron by
5.0 °C? ( cFe= 0.444 J/(g  °C)) a. | 2.2 J | b. | 4.4 J | c. | 0.44
J | d. | 0.89 J |
|
|
|
5.
|
Suppose 0.10 kJ of energy are removed from a 15 g sample of aluminum. What will
happen to the temperature? ( caluminum = 0.900 J/(g  ° °C)) a. | decrease by 7.4 °C | b. | increase by 1.35
°C | c. | increase by 7.4 °C | d. | decrease by 1.35 °C |
|
|
|
6.
|
What quantity of energy is required to increase the temperature of 1.0 kg
block of ice from –5.0 °C to –1.0 °C? ( cice = 2.03 J/(g
 °C)) a. | 120 J | b. | 8.1 kJ | c. | impossible to
calculate since ice always has a temperature of 0 °C | d. | 10.2
kJ |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which equation correctly summarizes the information in this figure? 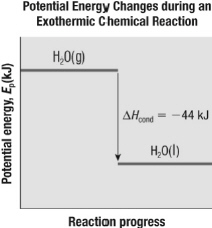 a. | H2O(g) ® H2O(l) + 44
kJ | b. | DHcond = 44 kJ | c. | H2O(g)
® H2O(l), DH = 44
kJ | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
8.
|
Given the equation:
N2(g) + 2 O2(g) ® 2 NO2(g), DH = 68
kJ
Which of the following is correct?
a. | 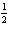 N2(g) + O2(g) ® NO2(g), DH= –68
kJ N2(g) + O2(g) ® NO2(g), DH= –68
kJ | b. | 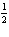 N2(g) + O2(g) ® NO2(g), DH = 68
kJ N2(g) + O2(g) ® NO2(g), DH = 68
kJ | c. | NO2(g) ® 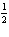 N2(g) +
O2(g), DH = –34 kJ N2(g) +
O2(g), DH = –34 kJ | d. | NO2(g)
® 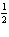 N2(g) + O2(g), DH = 34 kJ N2(g) + O2(g), DH = 34 kJ |
|
|
|
9.
|
Find DH for the reaction below, given the
following reactions and DH values:
N2O4(g) + 2 NO2(g)
2 NO2(g) ® 2 O2(g) + N2(g), DH = –33.9 kJ
2 O2(g) + N2(g) ® N4O4(g), DH = 4.8
kJ
a. | 39 kJ | b. | 29 kJ | c. | –39 kJ
| d. | –29 kJ |
|
|
|
10.
|
Use the graphs below to determine the enthalpy of reaction for the conversion of
butane, C 4H 10, to butanol, C 4H 9OH. 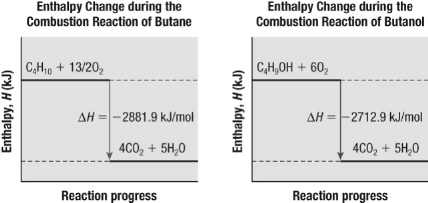 a. | 169 kJ/mol | b. | –169 kJ/mol | c. | 5594.8
kJ/mol | d. | –5594.8 kJ/mol |
|
|
|
11.
|
What is the correct formation reaction equation for sulfuric acid?
a. | H2(l) + S(l) +2 O2(l) ®
H2SO4(l) | b. | H2(g) + SO4(g) ® H2SO4(l) | c. | H2(g) +
S(s) + 2 O2(g) ® H2SO4(l)
| d. | H2(g) + S(s) + O2(g) ®
H2SO4(l) |
|