Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The following data were obtained for the reaction represented by the equation
2 SO 2(g) + O 2(g) ®
2SO 3(g) | Time (s) | [SO2(g)] (mol/L) | | 0 | 0.1000 | | 10 | 0.0078 | | 15 | 0.0053 | | 20 | 0.0040 | | |
What is the average rate of disappearance of
sulfur dioxide gas, SO 2(g), for the first 15 s? a. | 0.0005 0 mol/(L s) s) | b. | 0.0063 mol/(L s) s) | c. | 0.0070 mol/(L s) s) | d. | 0.10 mol/(L s) s) |
|
|
|
2.
|
This graph best represents the changes in concentration associated with which
chemical reaction? 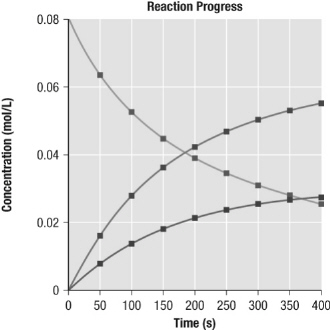 a. | 2 HCl (g) ® H2(g) + Cl2(g)
| b. | H2(g) + Cl2(g) ® 2 HCl
(g) | c. | 2 H2(g) + O2(g) ® 2
H2O (g) | d. | 2 SO3(g) ® 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) |
|
|
|
3.
|
From the given graph, which of the following statements is true? 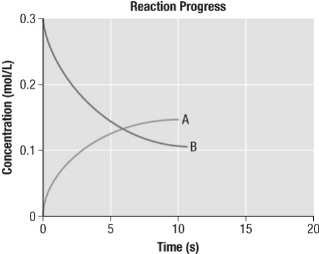 a. | In this reaction, A is the product and it appears twice as fast as B
disappears. | b. | In this reaction, A is the reactant and it disappears twice as fast as B
appears. | c. | In this reaction, A is the reactant and it disappears half as fast as B
appears. | d. | In this reaction, A is the product and it appears half as fast as B
disappears. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Copper metal will react with silver nitrate solution to produce silver metal and
blue copper(II) nitrate solution. Which of the following will affect the rate of this
reaction?
a. | changing the concentration of one of the silver nitrate solution | b. | cleaning the surface
of the copper with steel wool before the reaction | c. | changing the temperature of the
system | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
5.
|
Catalysts are
a. | consumed in a chemical reaction | b. | large protein molecules | c. | produced by living
organisms | d. | used to change the rate of a chemical reaction |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which of the following correctly summarizes collision theory?
a. | Reactant particles must collide with proper orientation and enough energy to
react. | b. | Atoms, ions, and molecules must collide with correct orientation in the
presence of a catalyst. | c. | Reactant particles must collide with correct
orientation. | d. | Atoms, ions, or molecules must collide at high
temperature. |
|
|
|
7.
|
What is activation energy?
a. | the minimum amount of energy the reactants must have for a collision to be
effective | b. | the difference in energy between reactants and products | c. | the amount of energy
required to break the bonds of reactants | d. | the amount of energy required to overcome the
electrostatic repulsions between reactant molecules |
|
|
|
8.
|
What will happen as the temperature of a system increases?
a. | The activation energy of the system will increase, causing an increased reaction
rate. | b. | All the particles will have more kinetic energy, causing more effective collisions.
This will increase the reaction rate. | c. | The average kinetic energy of the particles
will increase, causing more frequent collisions. This will decrease the reaction
rate. | d. | The motion of the particles increases, causing more effective collisions, resulting
in an increased reaction rate. |
|
|
|
9.
|
If the rate law for a reaction is determined to be rate =
k[X]1[Y]2[Z]0, then the order
of the reaction is
|
|
|
10.
|
If the rate law for a reaction is determined to be rate =
k[X]1[Y]2[Z]0, then the order
of the reaction with respect to Y is
|
|
|
11.
|
a. | rate = k[A][B] | b. | rate =
k[A] | c. | rate =
k[B] | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
12.
|
If the rate law for a reaction is determined to be rate =
k[X]1[Y]2[Z]0, then doubling
the initial concentration of Y will
a. | quadruple the rate of the reaction | b. | double the rate of the
reaction | c. | halve the rate of the reaction | d. | have no effect on the rate of the
reaction |
|
|
|
13.
|
The rate law for a reaction is determined to be rate =
k[X]1[Y]2[Z]0. If then initial
concentration of Z is doubled, then the rate of the reaction will
a. | quadruple | b. | halve | c. | double | d. | stay the same |
|
|
|
14.
|
For the reaction represented by A + B + C ® D +
E, the following data were obtained: | Run | [A]
(mol/L) | [B] (mol/L) | [C] (mol/L) | Initial rate (mol/(L s)) s)) | | 1 | 0.0025 | 0.0015 | 0.0020 | 4.50 ´
10–4 | | 2 | 0.0050 | 0.0015 | 0.0020 | 9.00 ´
10–4 | | 3 | 0.0025 | 0.0030 | 0.0020 | 4.50 ´
10–4 | | 4 | 0.0025 | 0.0015 | 0.0060 | 4.05 ´
10–3 | | | | | |
What is the rate law for this reaction?
a. | rate = k[A] | b. | rate =
k[A][B][C]2 | c. | rate =
k[A]2[B][C] | d. | rate =
k[A][C]2 |
|