Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which is most likely a property of a non-metal?
a. | ductile | b. | malleable | c. | good conductor or
thermal energy | d. | dull appearance |
|
|
|
2.
|
Gold and silver are ideal for jewellery because they are
a. | inexpensive to obtain | b. | resistant to corrosion | c. | very hard and
brittle | d. | good electrical conductors |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which of the following is an element?
a. | ammonium chloride | b. | sodium fluoride | c. | methane | d. | boron |
|
|
|
4.
|
The following sequence shows the size of the diameter of atoms for Period
2:
Li > Be > B > C > N > O > F
If Period 3 follows a similar pattern,
where would you expect silicon to fit in with respect to diameter?
a. | between Al and P | b. | between Na and Mg | c. | between S and
Cl | d. | between O and F |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which element is likely to react violently with water?
a. | beryllium | b. | carbon | c. | cesium | d. | sulfur |
|
|
|
6.
|
Athletes eat oranges and bananas because they are a good source of
a. | copper | b. | potassium | c. | nitrogen | d. | calcium |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which element helps to form strong bones and teeth?
a. | fluorine | b. | sodium | c. | calcium | d. | iodine |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which element glows bright red when an electric current is passed through
it?
a. | helium | b. | neon | c. | argon | d. | krypton |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which statement is correct?
a. | Be is more reactive than Li. | b. | Na is more reactive than
Mg. | c. | O is more reactive than F. | d. | S is more reactive than
Cl. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Rutherford’s gold foil experiment showed that
a. | atoms have a tiny, positively charged nucleus | b. | atoms are mostly
solid | c. | electrons crowd tightly together at an atom’s centre | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which characteristic was likely to have caused Rutherford to choose gold for his
“gold foil” experiments?
a. | Gold is readily obtained in a pure form. | b. | Gold can be pounded
into very thin sheets. | c. | Gold is usually inexpensive to
obtain. | d. | Gold conducts heat and electricity well. |
|
|
|
12.
|
In the diagram shown of a planetary atom, the indicated particle is 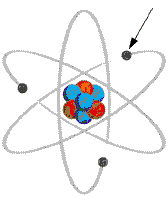 a. | the nucleus | b. | a proton | c. | an
electron | d. | a neutron |
|
|
|
13.
|
How is Bohr’s model of electron orbits around an atomic nucleus different
from the orbits of planets around the Sun?
a. | Electrons are repelled by the nucleus, but planets are attracted to the
Sun. | b. | Electrons attract one another; planets repel one another. | c. | Electrons orbit in
different planes; all planets (except Neptune) orbit concentrically in the same
plane. | d. | Planets orbit in different directions; electrons orbit in the same
direction. |
|
|
|
14.
|
If an atom has six protons, six electrons, and eight neutrons it must be an
isotope of
a. | carbon | b. | oxygen | c. | silicon | d. | magnesium |
|
|
|
15.
|
If an atom has two protons, two electrons, and two neutrons, it must be an
isotope of
a. | beryllium | b. | carbon | c. | helium | d. | lithium |
|
|
|
16.
|
An atom has a mass number of 20 and it contains 10 neutrons. What element must
it be?
a. | calcium | b. | neon | c. | boron | d. | More information is
needed. |
|
|
|
17.
|
An atom of phosphorus has a mass number of 31. How many neutrons must it
contain?
a. | 16 | b. | 15 | c. | 31 | d. | More information is
needed. |
|
|
|
18.
|
The reason cesium is more reactive than rubidium is that
a. | cesium is more non-metallic than rubidium | b. | cesium has more
electrons in its outer orbit than rubidium | c. | cesium has fewer electrons in its outer orbit
than rubidium | d. | cesium’s outer orbit is farther from the nucleus than rubidium’s outer
orbit |
|
|
|
19.
|
The diagram shows a neutral atom. Which element would have atoms with similar
chemical properties? 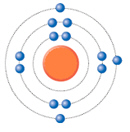 a. | gallium | b. | silicon | c. | calcium | d. | phosphorus |
|
|
|
20.
|
Many dry cell batteries contain an electrically conductive central rod that is
made of
a. | graphite | b. | diamond | c. | charcoal | d. | clay |
|
|
|
21.
|
The portion of the Periodic Table shown gives the melting points of selected
elements in degrees Celsius. Which would be a reasonable prediction for the melting point of
germanium, Ge? C
3570 | N
-210 | O
-219 | F
-218 | Si
1414 | P
44 | S
119 | Cl
-101 | Ge
| As
817 | Se
217 | Br
-7 | Sn
232 | Sb
631 | Te
450 | I
114 | | | | |
a. | greater than 1414 oC, but less than 3570 oC | b. | greater than 232
oC, but less than 817 oC | c. | less than 817 oC, but greater than
232 oC | d. | less than 1414 oC, but greater than
817 oC |
|